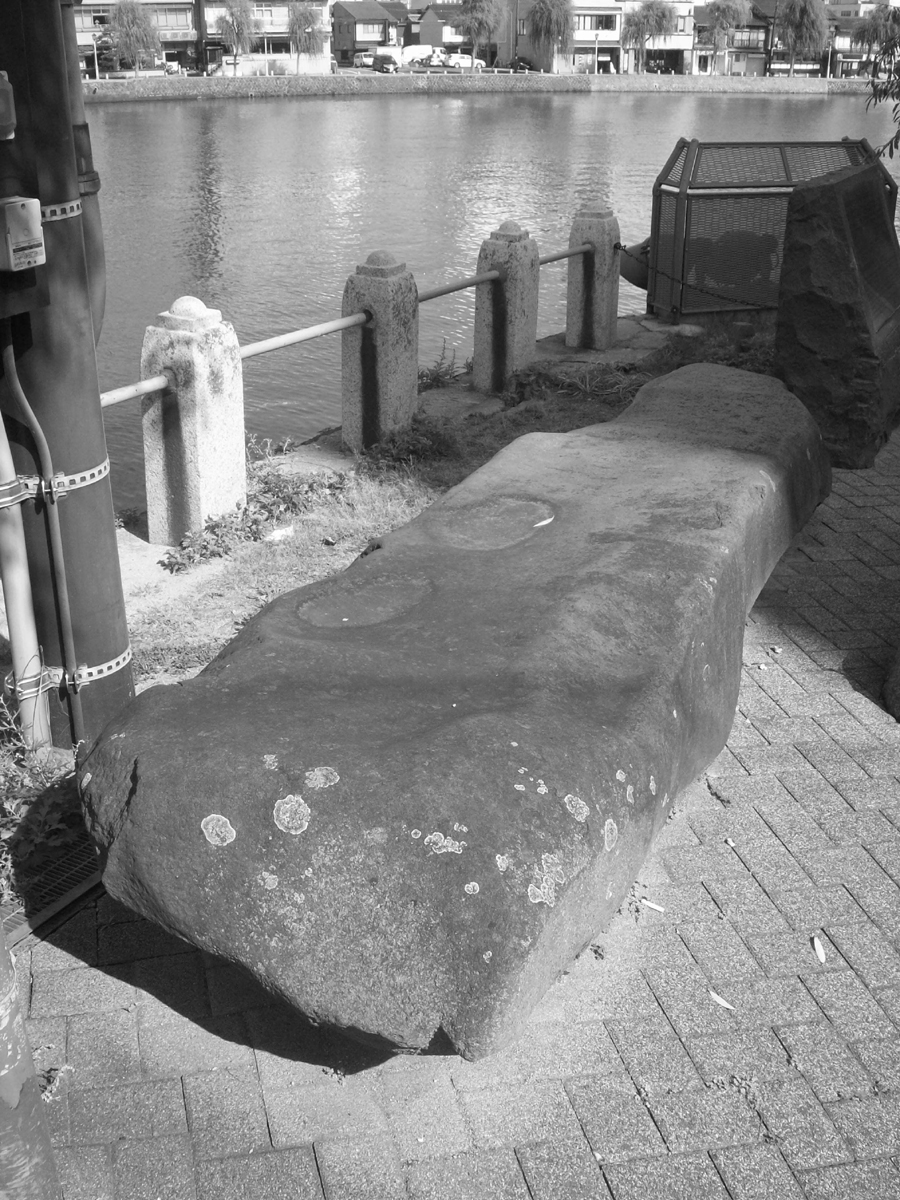
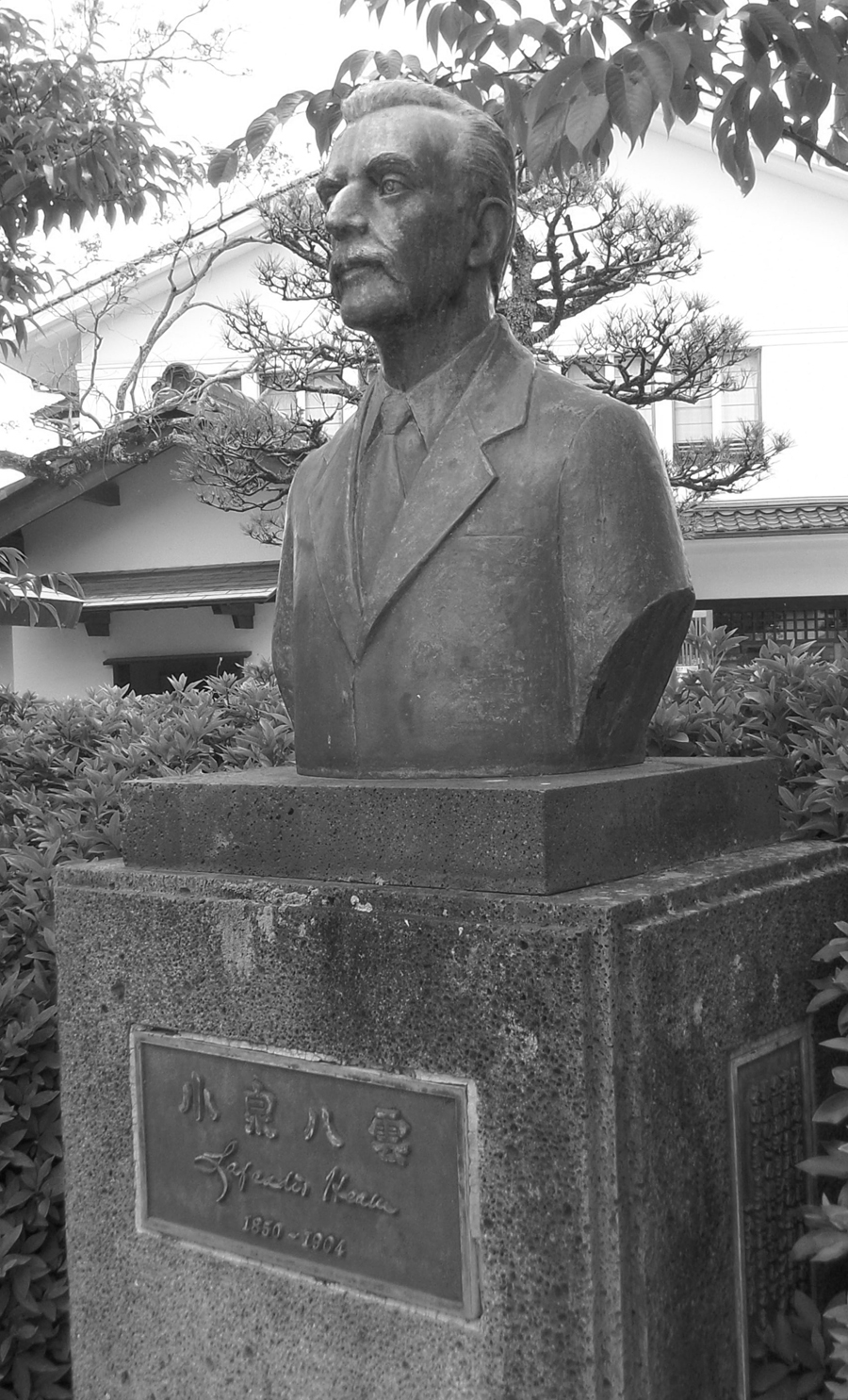
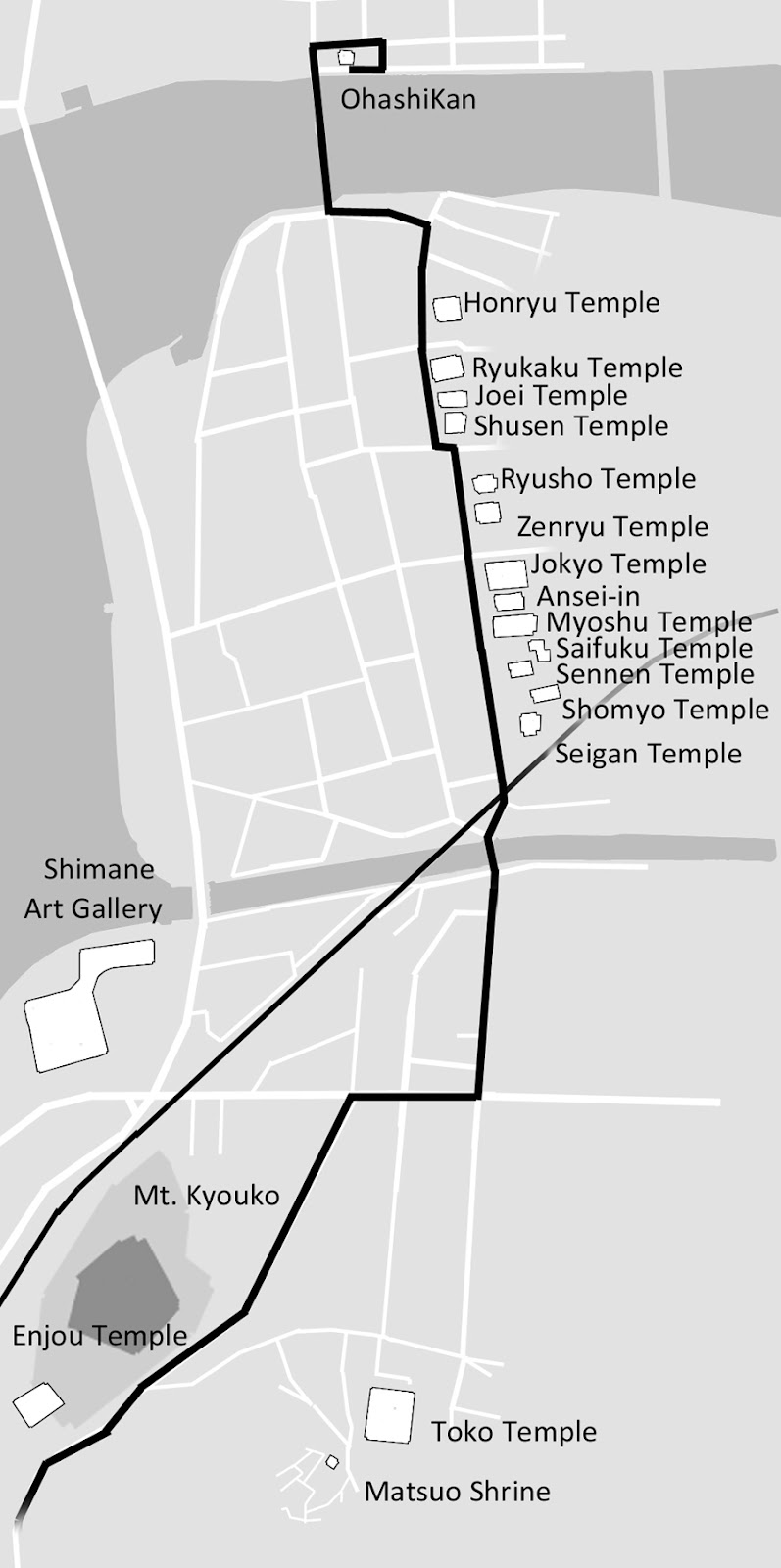
Lafcadio Hearn’s last visit to Matsue was in 1897, just before he moved to Tokyo. He wrote about it for the periodical Atlantic Monthly where he explained his trepidation
Sunday 13 November 2022
Walking with a Victorian through Meiji Japan
Lafcadio Hearn’s last visit to Matsue was in 1897, just before he moved to Tokyo. He wrote about it for the periodical Atlantic Monthly where he explained his trepidation
Tuesday 25 October 2022
My predictions for Red Dead Redemption 3
Also, further along the coast, is a right angled patch of discoloured ground which might have been part of a yard, indicating that a settlement was once going to be here.
Finally, there is an area opposite Annesburg with a large number of wolves and cougars which I wonder might have been part of a challenge to kill them off before the gang was able to set up camp there.
Thursday 8 September 2022
Have you been in a ganzfeld experiment?
Sunday 14 August 2022
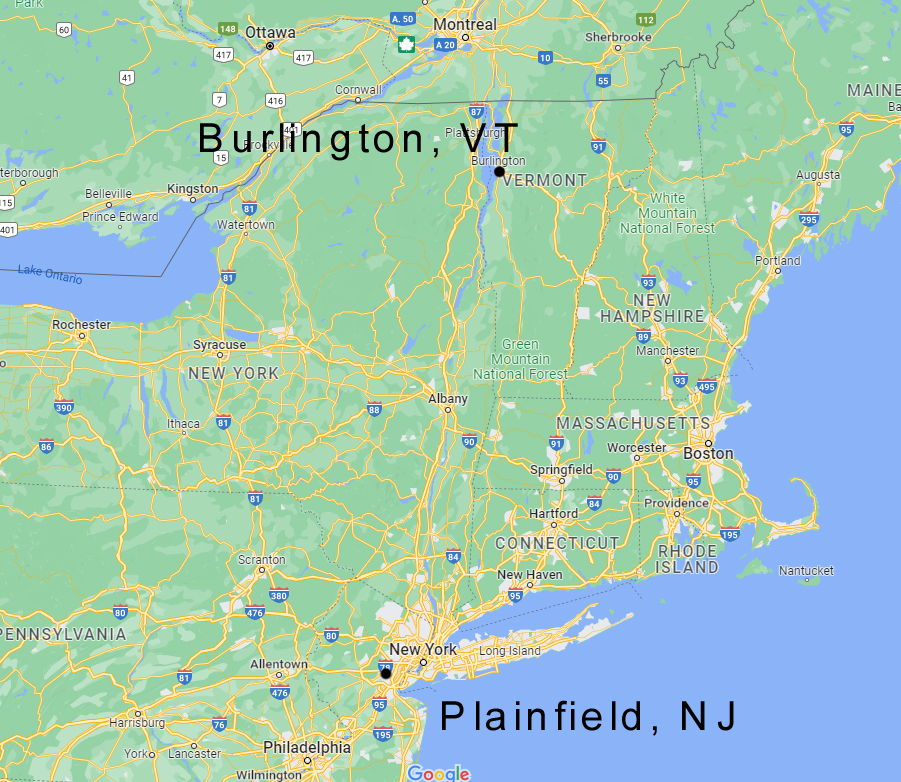
The curious case of Charles Brewin and Frank Johnson
This encounter was described in a local paper where a friend of Frank Johnson, Dr Buchanan, took particular note of it. His father, Mr Buchanan was a chaplain in Burlington and he thought his father might know Charles Brewin. And then, on June 30th, he got a call from Johnson’s landlady Mrs Dunn to come at once: her tenant had woken up saying his name was Charles Brewin and he didn’t know where he was, apparently under the impression that he’d left Burlington the previous day.
He went at once, with his father, and found the gentleman in question pale and weak but otherwise fine, now answering to the name of Brewin and seemingly having no memory of the past four years. Brewin and Mr Buchanan did know each other and he was later reunited with his family and, initially, returned to Burlington. After a little over a week, he and his family moved back to Plainfield and returned to the job he’d held previously when he was Frank Johnson.
That was a brief summary of the case as described by James Hyslop in 1913, vol 7, no 4 of the Journal of the American Society for Psychical Research. There are some contemporary newspaper articles that paint a slightly different picture (ie, that Brewin’s memory returned while he was in hospital) but the number of witnesses Hyslop spoke to lends it the most credibility.
Tuesday 5 July 2022
Remote viewing the Iranian Hostage Crisis 1979-81
The Iranian Hostage Crisis began on 4 November 1979 and was initially an anti-US demonstration in the Iranian capital of Tehran. Students, angry at the US agreeing to give medical treatment to the deposed and exiled Shah of Iran, occupied the grounds and buildings of the US Embassy, holding the staff there hostage.
This was not the first such demonstration in Iran that year and, although the US authorities were angry at the situation, it was assumed that it would only last a few days at most. However, when the Ayatollah Khomeni praised the actions of the students, it became something more important and the occupation continued, with 52 hostages being held for 444 days.
The remote viewing project, then called Grill Flame, began work on the hostage crisis within a month and continued to work on it for almost all of the time that Americans were in captivity: the last session is dated 13 January 1981 and the hostages were released one week later.
I wrote a book about the entire crisis called America’s Imaginary Hostage Crisis so if you’re interested in a deep dive into the data, then this is definitely recommended…
But for this blog, I’d like to assess the claims of success that you often see reported in articles or books.
The first is Joe’s recalling of the team being called into a special session on the day the occupation began.
The beginning of the crisis
In the early part of November 1979, I received a call at 4:00 A.M. asking me to report directly to the office [...] So, I arrived not knowing that the American Embassy located in Tehran, Iran, had been invaded by Iranian revolutionaries. It was still dark when all six permanent and part-time remote viewers joined the operations officer, Fred, in the office. He said it was going to sound like a strange request, but that a number of Americans had been taken hostage in a location overseas, and they needed our help in identifying them. He then threw a pile of a more than a hundred photographs onto the tabletop—tell us which are the hostages and which are not. He left the room and left us to the problem.
McMoneagle, Joseph. The Stargate Chronicles: Memoirs of a Psychic Spy: The Remarkable Life of U.S. Government Remote Viewer 001 . Crossroad Press. Kindle Edition.
Occasionally he recounts this story in talks and presentations, sometimes with the addition that he got it 100% correct.
The story is problematic for a couple of reasons. First, the US authorities knew exactly who was on the US embassy compound at the time the Iranians took over. Indeed, embassy staff in Tehran were calling Washington to keep the US government informed as the Iranians were arriving. Secondly, as mentioned before, this had happened before (in February 1979 the US Embassy had been occupied in an almost identical event) so the initial reaction to the actions of the students was not one of panic. The US authorities were confident that, after the students had been given some publicity, the Iranian police would move in and clear the compound.
So there’s no reason for an early morning session as described. It doesn’t exist in the declassified articles, nor is it included in lists of sessions or summaries of notable events. So it was either totally unofficial, not even sanctioned by the Grill Flame management, or it didn’t happen at all.
Operation Eagle Claw
Often in articles regarding Grill Flame and the hostage crisis, their role in the operation to rescue the hostages is mentioned. This military plan called Operation Eagle Claw took place in late April 1980, at a time when all of the hostages were still held in the embassy compound.
On 23 April, the remote viewing team were ordered to leave the Fort Meade site, where they were based, and move into three rooms booked in the Best Western Motel. For the next two days they’d run a grueling series of sessions targeted at different parts of the Embassy: twenty sessions in under forty hours.
The army operation taking place in Iran at this time ended in tragedy. Faulty equipment meant the mission was aborted and then, as they were about to return, a sandstorm whipped up and in the ensuing confusion, a helicopter crashed into a plane and eight servicemen died while the rest retreated back to safety.
During the session at the motel, two remote viewers reported seeing something violent. On 24 April at 4pm, Fern described a “quick raid” while describing the Deputy Chief Mission Residence (area I).
“[..] Report the activity as two o’clock in the morning.”
“It’s one of complete mayhem.”
“Tell me what makes you say that.”
“I don’t know.”
“Report the raw imagery to me.”
“People scurrying. Guards scurrying from their cots.”
“Go on.”
“Just a quick impression of a very foreboding quick action.”
“All right. Move in time again one more hour in the future. Three o’clock in the morning. Three o’clock in the morning.”
“I can’t get rid of this imagery of a quick raid.”
Endersby, “America’s Imaginary Hostage Crisis” p98, Kindle
And the second example is often credited to Nancy Stern although it was actually Hartleigh Trent who conducted session CCC84. In her book “Phenomenon” Annie Jacobson writes:
Declassified documents indicate that on April 24, 1980, Nancy S. was conducting Remote Viewing (RV) Session CCC84 when she broke down. The tasker noted, “Admin note 0300 Hours in Iran,” or at 3:00 a.m. local time, Nancy S. reported she was having trouble getting the target she’d been sent to, which was a building in Tehran code-named India. Instead, she said she saw “an attacking force of some kind.” She apologized and stated that perhaps she was “hallucinating.” What she saw was “weird and illogical” but “very vivid, horrible. Like a bad dream…” Her descripion was of “Big chest, big big gorillas. Great big chest beating gorilla leading these apes… they had tiny 9 inch long rockets, hundreds of them.” She apologized again and said she’d “never lost control like this before.”
Putting to one side any confusion between Nancy or Hartleigh, the fact is that the remote viewing sessions had twice described violent or disturbing scenes. But this was because they weren’t blind to the target, nor to the aims of Operation Eagle Claw. They’d been fully briefed on the topic and so it is not surprising that scenes of armed exchanges would be reported. It’s worth noting, however, that the US forces retreated long before any chance at engaging with enemy troops could take place.
The news about the tragic end of Operation Eagle Claw broke during two sessions being run simultaneously. Both were cut short as the remote viewing team were brought together to watch the TV news. According to McMoneagle, Nancy was deeply upset at this and, in fact, she soon left the team and would never complete another remote viewing session.
Richard Queen
The next most famous claim concerns Keith Harary’s description of a session he undertook in July 1980.
I received an urgent morning call asking me to report to SRI. I met with a tall, expressionless man who served me a cup of hot coffee before we retired to the white room and got to work.
"We have a person who needs a description," the monitor said, offering me not a clue. Though I hardly understood the process, the question triggered a cascade of impressions about a person in a debilitated state of health. "He seems to be suffering from nausea," I said. "One side of his body seems damaged or hurt." I wondered whether the person I was describing might be some business person or a head of state.
"Where will he be in the next few days?" the monitor asked, again without inflection. I suddenly felt the sensation of sitting on an airplane that was taking off.
"On an airplane," I said.
The target turned out to be the hostage Richard Queen, held by Iranian militants and now desperately ill with multiple sclerosis that affected his nerves on one side. In part due to my input, I was later informed by contacts at SRI, President Carter dispatched a plane to bring Queen home.
https://www.psychologytoday.com/gb/articles/200411/confessions-star-psychic
Keith Harary was working for SRI in July 1980 and he had recently run a number of sessions against the Hostage Crisis. But SRI work focused on the hostages is largely missing from the declassified archives. Any contemporary notes from this particular session targeting Richard Queen are absent, possibly because it wasn’t part of the Grill Flame Project. The first time it is mentioned is in 1983, in an overview of the Grill Flame project when it is listed among a number of “successful viewings for the DoD/intelligence community”. But there are no further details. And Harary himself has issues with how psychic his vision had been.
“Were my impressions psychic? The hostages had been flooding the news for months.
Reports about Queen's health problems, including the issue of "a lame shoulder," had been in the news as well. I don't know whether such reports infiltrated my unconscious without my realizing it, but it would make sense to consider that possibility before the paranormal alternative.
https://www.psychologytoday.com/gb/articles/200411/confessions-star-psychic
Conclusion
Ultimately, the efforts of the remote viewing team were not well-received and a report written after the crisis was over stated:
“Comparison of the reports with returnee debriefings revealed a very low correlation between actual hostage locations/ conditions and inferences drawn from Grill Reporting. Only seven reports could be positively correlated with actual location or condition. Approximately 59
reports revealed a possible or partial correlation.
However, these same reports often included erroneous data. Sixteen reports contained inconclusive data making correlation highly subjective. Eight reports were noted as being poor from an administrative/ procedural standpoint and therefore being of no value. One hundred and twelve reports were found to be entirely incorrect.”
https://archive.org/details/CIA-RDP96-00788R001000340002-3
So, how much of the data produced by Grill Flame was used operationally? None. The entire project had been for training purposes, something that the remote viewers were not aware of. But by now, despite the results, Grill Flame had other projects to work on and it seems that simply being involved in the Hostage Crisis had raised its profile and secured its funding for another few years, at least.
Friday 20 May 2022
Remote viewing the hostage William F Buckley 1984
Monday 2 May 2022
Remote Viewing the hostage LTC William Higgins 1988-1989
As such, the DIA arranged a follow up session in which Angela (and two other RVers) was told to focus on that area. In the typed notes, the area she chose is labeled “Y” with the note that “(Y appears to be an open field).” However, Angela predicts his imminent move to another area. The next time she specifies an area for Higgins, it is a long way from Arab Salim.